Imagine a world without the exquisite pleasure of savoring a perfectly aged glass of wine. A world where the vibrant notes are muted, and the delicate aromas are lost. To ensure that every sip is a delight, it is crucial to understand the impact of temperature on the taste and longevity of wine. Are you curious to discover the best temperature for wine storage and how temperature variation can influence your favorite bottle of red or white? Stay with us as we uncork the secrets of the ideal storing conditions for wine.
Temperature and Wine Storage
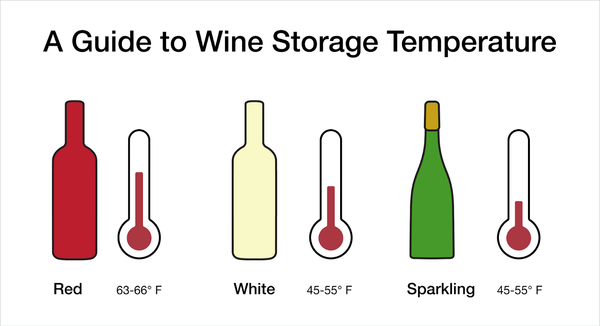
Ideal temperature for wine storage
The ideal temperature for wine storage is around 55 degrees Fahrenheit (13 degrees Celsius). This temperature provides a balance between preserving the wine’s integrity and allowing it to age gracefully. It is important to maintain a consistent temperature within this range, as fluctuations can have adverse effects on the taste and longevity of the wine.
Optimal temperature range for red wines
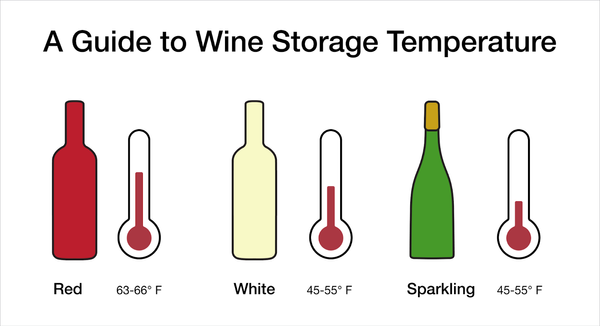
For red wines, the optimal temperature range for storage is between 55 and 65 degrees Fahrenheit (13 and 18 degrees Celsius). This range allows the wine to age slowly and develop its complex flavors. Red wines that are stored at higher temperatures may age too quickly, resulting in a flat or cooked taste. On the other hand, storing red wines at lower temperatures can impede the aging process and prevent the wine from reaching its full potential.
Optimal temperature range for white wines
White wines are generally more delicate than red wines and require slightly cooler temperatures for storage. The optimal temperature range for white wines is between 45 and 55 degrees Fahrenheit (7 and 13 degrees Celsius). Storing white wines at higher temperatures can lead to premature aging and the loss of fresh and fruity flavors. Cooler temperatures help to preserve the vibrant characteristics of white wines and keep them in optimal condition for longer periods.
Effect of temperature variation on wine
Temperature variation can have a significant impact on the taste and quality of wine. Fluctuations in temperature, especially rapid changes, can cause the expansion and contraction of the liquid inside the bottle. This can lead to a phenomenon called “maderization,” where wine begins to develop oxidized, nutty, or cooked flavors. Temperature variations can also disrupt the aging process, resulting in an imbalanced and less enjoyable wine drinking experience.
The role of temperature in aging wine
Temperature plays a crucial role in the aging process of wine. Slow and controlled aging allows the wine to develop its complex flavors and aromas over time. When the wine is stored at the ideal temperature, the chemical reactions that occur during aging are more balanced and harmonious. Higher temperatures can accelerate the aging process, often at the expense of the wine’s quality. Conversely, lower temperatures can slow down aging, delaying the development of desirable characteristics.
Impact of temperature on wine flavors
Temperature has a profound influence on the flavors of wine. When served at the proper temperature, wine can showcase its true character. The balance of acidity and sweetness is particularly affected by temperature. Cooler temperatures can accentuate the acidity in wine, while warmer temperatures tend to enhance the perception of sweetness. Additionally, the extraction of tannins, which contribute to the structure and mouthfeel of wine, is influenced by temperature. Proper temperature control ensures that these flavors are presented in a harmonious and enjoyable manner.
Understanding Wine Storage
Why proper wine storage is important
Proper wine storage is essential for maintaining the quality and longevity of wine. Wine is a delicate and perishable product that can easily be affected by external factors, including temperature, humidity, light exposure, and ventilation. By storing wine under optimal conditions, we can ensure that it ages gracefully, preserves its flavors and aromas, and delivers a memorable experience when it is finally uncorked.
Factors that affect the quality of stored wine
Several factors can influence the quality of stored wine. In addition to temperature, humidity levels, light exposure, ventilation, and even the position in which the wine bottles are stored can all have an impact. Controlling these factors effectively can significantly enhance the wine’s quality and longevity.
Temperature as a critical storage factor
Temperature is arguably the most critical factor in wine storage. The chemical reactions that occur during aging are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Maintaining a consistent and optimal temperature is crucial to ensure that these reactions progress at the desired rate and produce desirable flavors and aromas. Proper temperature control also helps prevent the risk of wine faults and spoilage.
Relationship between temperature and wine chemistry
Temperature has a direct influence on the chemistry of wine. As the temperature rises, molecules within the wine become more energetic and react more rapidly. This increased activity can accelerate chemical reactions, resulting in more rapid aging and the potential for off-flavors to develop. Conversely, lower temperatures slow down chemical reactions, preserving the wine’s freshness and allowing for a more gradual and controlled aging process.
Effects of temperature swings on wine
Temperature swings can have detrimental effects on wine. Rapid changes in temperature, especially when they occur frequently, can subject the wine to stress and compromise its stability. This can lead to a loss of flavor and aroma compounds, as well as potential spoilage or the development of off-flavors. It is crucial to minimize temperature swings to protect the wine’s quality and ensure a consistent aging process.
Ideal Conditions for Wine Storage
Temperature considerations
When it comes to wine storage, maintaining a consistent temperature is key. As mentioned earlier, the ideal temperature for wine storage is around 55 degrees Fahrenheit (13 degrees Celsius). It is important to avoid significant deviations from this temperature, as it can impact the wine’s aging process and overall quality. Investing in a wine storage unit or cellar that allows for precise temperature control is highly recommended.
Humidity levels for wine storage
Humidity levels also play a role in wine storage. Ideally, the humidity should be kept between 60% and 70% to prevent the corks from drying out. When corks dry out, they can shrink, allowing air to enter the bottle and potentially spoil the wine. On the other hand, excessive humidity can lead to mold growth on the labels or even damage to the corks. Maintaining a moderate level of humidity is crucial for optimal wine storage conditions.
Light exposure and its impact on wine
Exposure to light, especially sunlight or fluorescent lighting, can be harmful to wine. Ultraviolet (UV) rays in light can cause chemical reactions in the wine that result in the degradation of flavor and aroma compounds. To minimize the impact of light, it is recommended to store wine in a dark or dimly lit area. Wine cellars or dedicated wine storage units often have low or no light, providing an ideal environment for wine to age undisturbed.
Importance of ventilation
Proper ventilation is necessary to ensure that wine can “breathe” and avoid musty or stale odors. Adequate air circulation helps prevent the build-up of unpleasant aromas that can seep into the wine and affect its quality. It is important to note that excessive ventilation or exposure to strong odors, such as in a kitchen or near chemicals, should be avoided as they may also impact the wine’s flavors.
Storing wine bottles horizontally
Storing wine bottles horizontally is a traditional practice that helps ensure the long-term quality of the wine. When the bottle is positioned horizontally, the wine maintains contact with the cork, which helps to keep it moist and prevent it from drying out. A dry cork can lead to oxidation and spoilage of the wine. By storing wine bottles on their side, you can help preserve the integrity of the wine and prolong its shelf life.
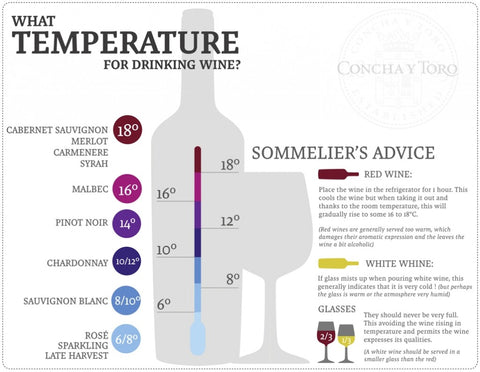
Optimal Temperature for Red Wines
Typical temperature range for red wines
Red wines are typically best enjoyed at a slightly warmer temperature compared to their storage temperature. The recommended serving temperature for most red wines is between 60 and 68 degrees Fahrenheit (15 and 20 degrees Celsius). This temperature range allows the red wine to showcase its full range of flavors and aromas.
Effects of higher temperatures on red wines
Exposing red wines to higher temperatures can have negative effects on their taste and quality. Higher temperatures can speed up the aging process and cause the wine to lose its vibrant fruit flavors and freshness. The wine may become flat, overly alcoholic, or develop cooked flavors. It is essential to store red wines at the appropriate temperature range and avoid subjecting them to excessive heat.
Effects of lower temperatures on red wines
Lower temperatures can also impact the taste and enjoyment of red wines. When served too cold, the aromas and flavors of red wine may be muted or suppressed. Tannins, which provide structure and mouthfeel, can appear more astringent and overpowering in colder temperatures. Allowing red wines to warm up slightly before serving (around 15 minutes out of the refrigerator) can help bring out their full potential.
Maintaining temperature stability for red wines
To ensure the optimal aging and serving conditions for red wines, it is important to maintain temperature stability. Temperature fluctuations can cause stress to the wine and lead to undesirable flavor development. Investing in a wine storage unit or cellar that offers temperature control features, such as a thermostat or temperature monitoring system, can help maintain stability and prolong the life of your red wines.
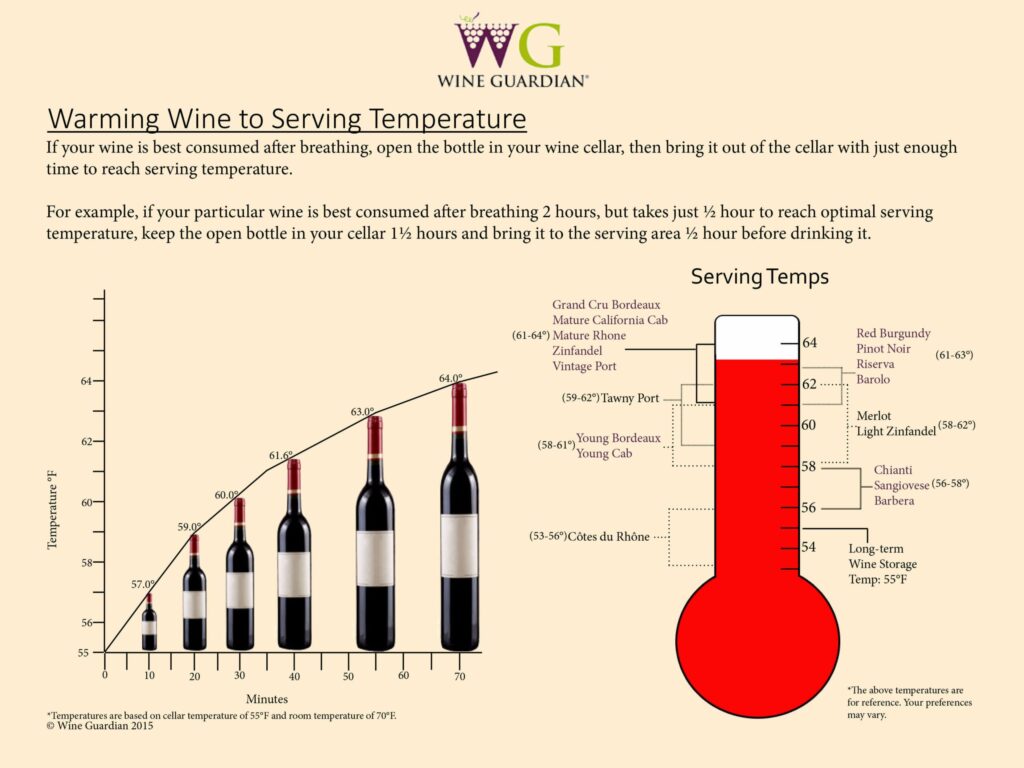
Temperature considerations for aging red wines
When aging red wines, it is crucial to choose an appropriate storage temperature. The ideal temperature for aging red wines is between 55 and 60 degrees Fahrenheit (13 and 15 degrees Celsius). This range encourages slow and controlled aging, allowing the flavors and aromas to develop harmoniously over time. Aging red wines at a slightly lower temperature can yield more graceful aging results.
Optimal Temperature for White Wines
Typical temperature range for white wines
White wines are generally served at cooler temperatures compared to red wines. The recommended serving temperature for most white wines is between 45 and 55 degrees Fahrenheit (7 and 13 degrees Celsius). This temperature range allows the white wine to showcase its delicate aromas and maintain its refreshing qualities.
Effects of higher temperatures on white wines
Storing white wines at higher temperatures can have a detrimental impact on their taste and quality. Higher temperatures can cause white wines to age prematurely, resulting in a loss of freshness and vibrant flavors. The wines may appear dull, lacking the crisp acidity and fruitiness that are characteristic of well-preserved white wines. It is crucial to store white wines at cooler temperatures to maintain their optimal quality.
Effects of lower temperatures on white wines
While lower temperatures can help preserve the freshness and acidity of white wines, serving them too cold can diminish their flavors and aromas. Extremely cold temperatures can make the wine taste flat and less expressive. Allowing white wines to warm up slightly before serving, around 10 minutes out of the refrigerator, can help unlock their full range of flavors and aromas.
Maintaining temperature stability for white wines
To ensure the longevity and enjoyment of white wines, it is important to maintain temperature stability. Fluctuations in temperature can disrupt the aging process and compromise the flavors and aroma development. A wine storage unit or cellar with temperature control features is highly recommended for storing white wines, as it allows for precise temperature regulation and stability.
Temperature considerations for aging white wines
When considering the aging of white wines, it is important to choose an appropriate storage temperature. The ideal temperature for aging white wines is between 50 and 55 degrees Fahrenheit (10 and 13 degrees Celsius). This temperature range promotes a slow and controlled aging process, allowing the wine to develop complex flavors while preserving its freshness. Aging white wines at a slightly lower temperature can help retain their vibrant and delicate characteristics.
Temperature Variation and Wine Quality
Temperature fluctuations and their impact on wine
Temperature fluctuations can have a significant impact on the quality of wine. Sudden changes in temperature can cause the wine to expand and contract, leading to potential leakage, spoilage, or the development of off-flavors. Frequent fluctuations can also accelerate the aging process and result in imbalanced flavors. It is crucial to minimize temperature fluctuations to preserve the quality and integrity of the wine.
Effects of rapid temperature changes on wine
Rapid temperature changes can shock the wine and negatively affect its taste and longevity. When exposed to sudden temperature shifts, the wine can undergo rapid oxidation, leading to a loss of freshness and fruitiness. Additionally, the expansion and contraction of the liquid inside the bottle can put pressure on the cork, potentially causing it to fail and allowing air to enter the bottle. To avoid these negative effects, storing wine in a controlled environment with minimal temperature fluctuations is essential.
Long-term consequences of inconsistent temperatures
Inconsistent temperatures over extended periods can have long-term consequences for the quality of wine. Fluctuations in temperature can disrupt the aging process, resulting in wines that may lack complexity or have unbalanced flavors. If wine is subjected to repeated temperature variations, it may become prematurely oxidized or develop off-flavors, significantly diminishing its enjoyment. Consistency in temperature is key to ensuring the wine retains its desired characteristics over time.
Potential wine faults caused by temperature variation
Temperature variation can contribute to the development of several wine faults. Maderization, which occurs when wine is exposed to excessive heat, can lead to oxidized flavors, giving the wine a nutty or cooked taste. Fluctuations in temperature can also exacerbate microbial activity, potentially resulting in the growth of spoilage organisms or yeasts that negatively affect the wine’s taste and aroma. By avoiding temperature variations, you can reduce the risk of these wine faults and maintain the quality of your wines.
Ways to mitigate the effects of temperature fluctuations
While total elimination of temperature fluctuations is challenging, there are measures you can take to mitigate their effects. Insulating your wine storage location and protecting it from direct sunlight can help maintain a more stable temperature. Consider investing in a wine storage unit or cellar with temperature control features for precise regulation. Reducing the frequency of temperature fluctuations by avoiding drastic temperature changes can also help minimize their impact on the wine. By implementing these strategies, you can better protect your wine collection and ensure a consistent and enjoyable drinking experience.
Temperature’s Role in Wine Aging
The importance of controlled aging temperatures
Temperature plays a vital role in the aging process of wine. Allowing wine to age at a controlled and consistent temperature can lead to the development of complex flavors and aromas. Temperature influences the rate of chemical reactions that occur during aging, impacting the wine’s evolution. A controlled aging temperature ensures that the wine ages gradually and harmoniously, preserving its balance and integrity.
Accelerated aging and high temperatures
High temperatures accelerate the aging process of wine, which can be detrimental to its quality. When subjected to excessive heat, the chemical reactions in wine occur at a faster pace, potentially leading to premature aging. The quickened aging process can result in the loss of freshness, the breakdown of delicate flavor compounds, and the development of off-flavors. It is crucial to avoid storing wine at high temperatures to prevent accelerated aging.
Slow aging and low temperatures
Conversely, lower temperatures can slow down the aging process of wine. When wine ages at a lower temperature, the chemical reactions occur at a more controlled rate, allowing the wine to develop complex flavors gradually. Slow aging preserves the freshness and balance of the wine, resulting in a more enjoyable drinking experience. Aging wine at a consistent and slightly lower temperature can enhance its aging potential and extend its shelf life.
Temperature’s influence on the development of flavors
Temperature plays a significant role in the development of flavors as wine ages. During aging, the complex reactions between various compounds in the wine give rise to new flavors and aromas. The temperature at which these reactions occur affects the formation and integration of these flavors. A controlled aging temperature allows for the gradual development and integration of flavors, creating a more harmonious and balanced wine.
Optimal temperature ranges for different wine styles and ages
Different wine styles and ages have varying optimal temperature ranges for aging. Full-bodied red wines, such as Cabernet Sauvignon or Syrah, typically benefit from aging at the higher end of the ideal temperature range (around 60-65 degrees Fahrenheit or 15-18 degrees Celsius). Lighter red wines, such as Pinot Noir or Beaujolais, age best at slightly lower temperatures (around 55-60 degrees Fahrenheit or 13-15 degrees Celsius). White wines, whether aged oaked or unoaked, generally age well at lower temperatures (around 50-55 degrees Fahrenheit or 10-13 degrees Celsius). By following these temperature guidelines, you can ensure that your aging wines reach their full potential.
Impact of Temperature on Wine Flavors
Taste perception and temperature
The temperature at which wine is served greatly influences taste perception. Cold temperatures can suppress flavors, making the wine taste less expressive and vibrant. Warmer temperatures can amplify the perception of flavors, allowing the wine’s characteristics to shine. It is essential to serve wine at the appropriate temperature to fully appreciate its flavors and enjoy a well-rounded tasting experience.
How temperature affects aroma and bouquet
Temperature also plays a crucial role in the perception of aromas and bouquet in wine. At cooler temperatures, the volatility of aromatic compounds is decreased, which can mute the wine’s aromas. As the temperature rises, more aromatic compounds are released, intensifying the wine’s bouquet. Serving wine at the right temperature allows these aromas to be fully expressed and enjoyed, enhancing the overall sensory experience.
Temperature’s impact on the balance of acidity and sweetness
Temperature significantly influences the balance of acidity and sweetness in wine. Cooler temperatures can enhance the perception of acidity, making the wine taste more vibrant and refreshing. Conversely, warmer temperatures can emphasize the perception of sweetness, providing a richer and more luscious mouthfeel. Serving wine at the appropriate temperature enables the perfect balance between acidity and sweetness, resulting in a harmonious and enjoyable taste.
Temperature’s influence on tannin extraction
Tannins, which come from grape skins, seeds, and stems, add structure and texture to wine. Temperature impacts the extraction of tannins during the winemaking process. Fermenting and aging red wines at warmer temperatures can extract more tannins, resulting in a wine with a more robust and astringent character. Cooler temperatures in the winemaking process can lead to the extraction of fewer tannins, resulting in a softer and more approachable wine. Understanding the role of temperature in tannin extraction allows winemakers to craft wines with the desired level of structure and balance.
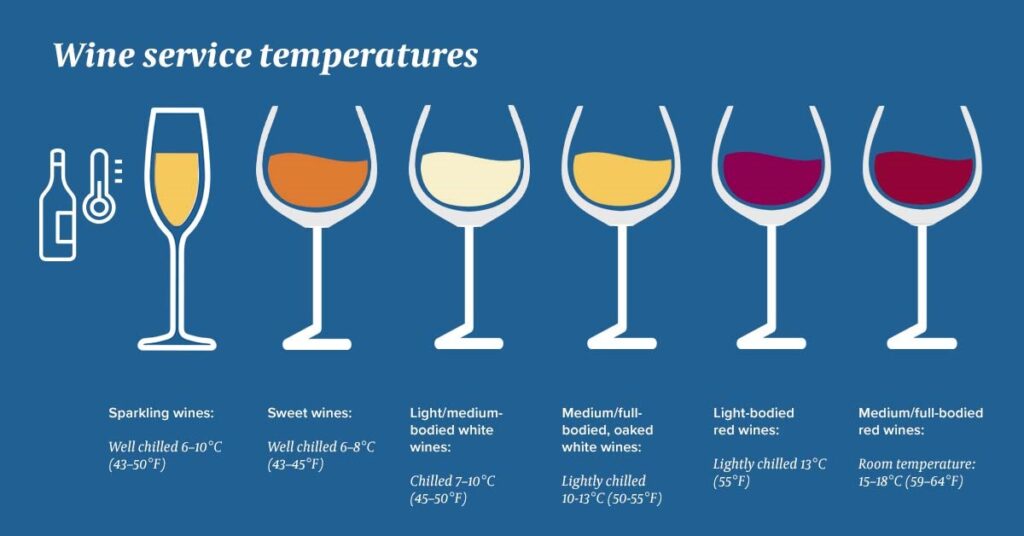
Temperature considerations for serving wine
To fully appreciate the flavors and aromas of wine, it is crucial to serve it at the proper temperature. Red wines benefit from being served slightly below room temperature, around 60-68 degrees Fahrenheit (15-20 degrees Celsius), to allow their flavors to develop fully. White wines, on the other hand, are best served chilled, around 45-55 degrees Fahrenheit (7-13 degrees Celsius), to preserve their freshness and delicate aromas. Sparkling wines and Champagne are often enjoyed at even lower temperatures, around 40-50 degrees Fahrenheit (4-10 degrees Celsius), to enhance their effervescence and liveliness. By serving wine at the appropriate temperature, you can savor the full spectrum of flavors and aromas that each bottle has to offer.

Proper Wine Storage Techniques
Investing in a wine storage unit
Investing in a wine storage unit is an excellent way to ensure proper wine storage conditions. These units are specifically designed to regulate temperature, humidity, and light exposure, providing an optimal environment for aging wine. Wine storage units often come with features such as adjustable temperature controls, UV-resistant doors, and humidity sensors to maintain the ideal storage conditions. By investing in a wine storage unit, you can safeguard your wine collection and enjoy it at its best.
Creating a dedicated wine cellar
For those with a larger wine collection or a greater passion for wine, creating a dedicated wine cellar is an exciting and worthwhile endeavor. A wine cellar offers the opportunity to customize the storage conditions to perfectly suit your collection. Careful consideration should be given to insulation, temperature control systems, humidity management, and lighting. Creating a wine cellar not only ensures proper storage but also adds aesthetic appeal and value to your home.
Alternative storage options for wine
If a dedicated wine storage unit or cellar is not feasible, there are alternative storage options that can still provide suitable conditions for your wine collection. A cool, dark closet or cupboard can work well for short-term storage. Using wine refrigerators or wine coolers can also be effective, especially for small to medium-sized collections. These appliances typically offer temperature control features and UV protection to maintain the quality of the wine. It is important to monitor the temperature and ensure that it remains within the appropriate range.
Tips for maintaining consistent temperatures
To maintain consistent temperatures for wine storage, it is essential to follow a few key tips. First, avoid exposing wine to direct sunlight or bright lighting, as this can raise the temperature and potentially spoil the wine. Additionally, ensure proper insulation and minimize temperature fluctuations by keeping the storage area away from sources of heat or cold, such as radiators or air conditioning vents. Regularly monitor the temperature using a thermometer or temperature control system to ensure it remains within the desired range.
Monitoring and controlling humidity levels
Humidity is another critical factor to consider for proper wine storage. Humidity levels should be maintained between 60% and 70% to prevent the corks from drying out. Investing in a hygrometer, a device that measures humidity, can help monitor and control humidity levels. If the humidity is too low, placing a pan of water in the storage area can help increase moisture. On the other hand, excessive humidity can be mitigated by using dehumidifiers or desiccant packets to absorb excess moisture. Regularly monitoring and adjusting humidity levels ensures that the corks remain intact and the wine is protected.
Conclusion
Proper wine storage temperature is essential for preserving the taste and longevity of wine. Whether you are storing red or white wines, understanding the optimal temperature ranges and the effects of temperature variation is crucial. Maintaining consistent and controlled storage conditions helps wine age gracefully, develop complex flavors, and maintain its overall quality. By investing in suitable wine storage solutions, such as storage units or cellars, and following proper storage techniques, you can ensure that your wine collection is well-protected and always ready to be enjoyed. Cheers!

