Have you ever wondered whether a dry space heater or a traditional heater is right for your home? It’s a question that puzzles many people, especially as the seasons change and temperatures drop. Let’s dive into the details, considering every angle to help you make an informed decision.

This image is property of blog.constellation.com.
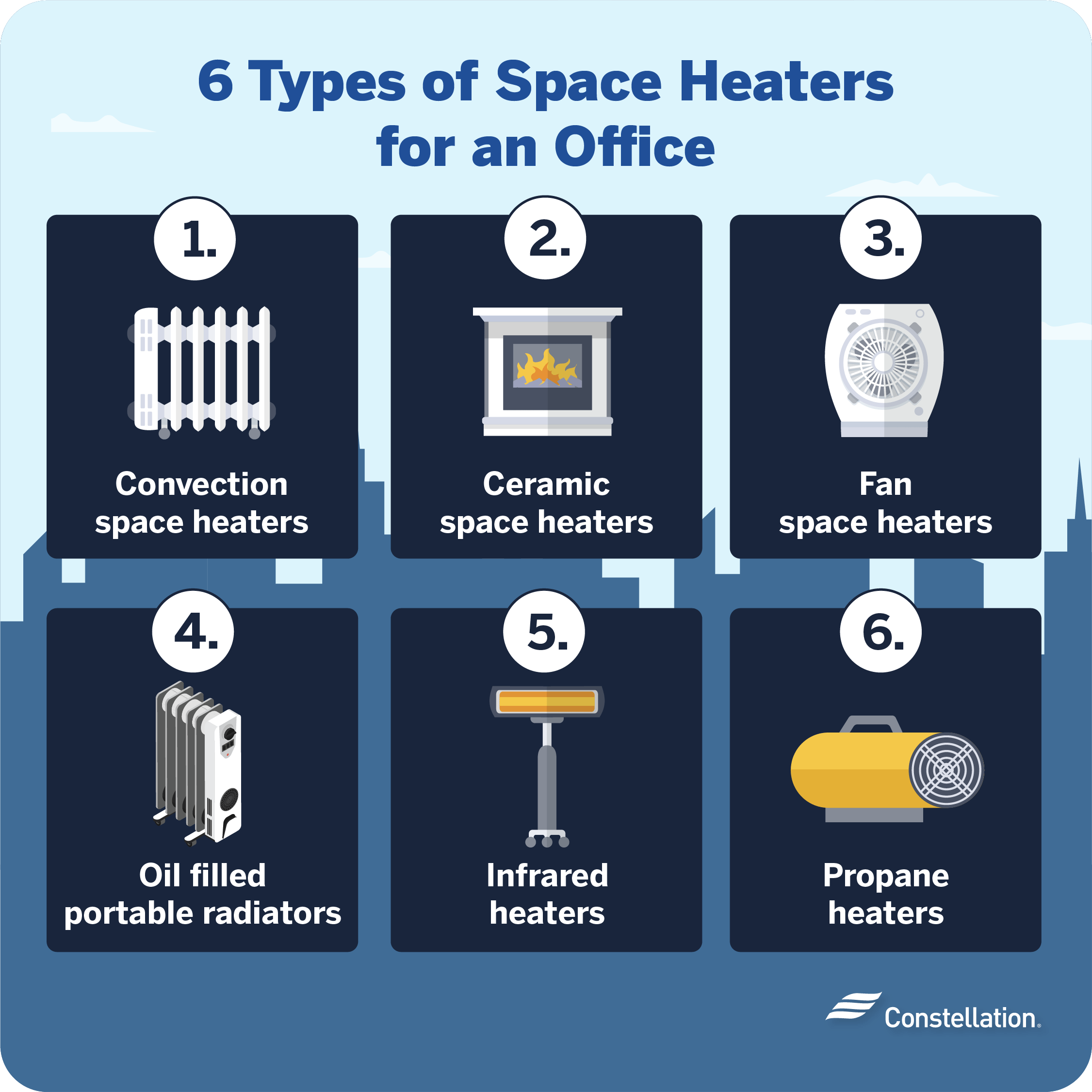
What Are Dry Space Heaters?
Before comparing them to traditional heaters, it’s essential to understand what dry space heaters are. Dry space heaters are a type of heater that uses infrared technology or ceramic heating elements to produce heat. These heaters don’t rely on conventional methods like burning fuel or using electric coils to warm the air. Instead, they heat objects and people directly, making the air feel warmer without changing the ambient temperature significantly.
Types of Dry Space Heaters
You have several options when it comes to dry space heaters:
- Infrared Heaters: Utilize infrared technology to produce heat by emitting infrared rays.
- Ceramic Heaters: Use ceramic plates and aluminum baffles to heat the surrounding air quickly and efficiently.
- Oil-filled Radiators: Filled with oil that heats up, releasing heat slowly and evenly.
Pros of Dry Space Heaters
Dry space heaters bring several benefits:
- Energy Efficiency: They direct heat where it’s needed, reducing energy waste.
- Instant Heat: You’ll feel the warmth almost immediately.
- Healthier Air: These heaters don’t dry out the air as much as traditional heaters.
- Noise Levels: Most models are pretty quiet, providing a more serene environment.
Cons of Dry Space Heaters
However, there are also some downsides:
- Limited Coverage: They are usually less effective in heating large spaces.
- Direct Line of Sight: The heat doesn’t distribute as widely, needing a direct line of sight to be effective.
- Initial Cost: Dry heaters can be more expensive upfront, though they often save money over time.
Traditional Heaters Explained
Traditional heaters come in various forms, but what they all share in common is using forced air, radiant heat, or convection methods to disperse warmth.
Types of Traditional Heaters
Here are the common types of traditional heaters:
- Central Heating Systems: Use furnaces or boilers to heat air or water and distribute it throughout the home.
- Electric Heaters: Utilize electric coils to heat the air.
- Gas Heaters: Burn natural gas or propane to generate heat.
- Wood Stoves and Fireplaces: Burn wood to produce radiant heat.
Pros of Traditional Heaters
Traditional heaters also offer numerous advantages:
- Wide Coverage: Efficiently heat large or multiple rooms.
- Consistent Warmth: Offer a more uniform heating experience.
- Variety: Numerous options to fit different budgets and needs.
- Longevity: Designed to last for many years, offering stable, reliable performance.
Cons of Traditional Heaters
However, they too have their drawbacks:
- Energy Consumption: Often less energy-efficient than dry space heaters.
- Air Quality: Can dry out the air, potentially irritating your skin and respiratory system.
- Noise: Some traditional heaters, especially forced air systems, can be noisy.
- Maintenance: Regular upkeep like changing filters and checking for leaks is necessary.

This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Comparing Efficiency
One of the biggest considerations is energy efficiency. After all, you don’t want to waste money on heating your home.
Energy Efficiency of Dry Space Heaters
Dry space heaters like infrared and ceramic models often boast high energy efficiency. They heat up quickly and distribute heat directly to the objects and people in their path, minimizing waste. This directly translates to lower electricity bills, making them ideal for smaller spaces or targeted heating.
Energy Efficiency of Traditional Heaters
On the other hand, traditional heaters generally consume more energy. Systems like central heating are designed to heat larger areas uniformly, which can lead to higher operational costs. While newer models are increasingly energy-efficient (especially those with programmable thermostats), they’re generally still more energy-intensive than dry space heaters.
Energy Comparison Summary
| Feature | Dry Space Heaters | Traditional Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Medium to High | Low to Medium |
| Operating Cost | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Medium to Low |
| Best For | Small or single rooms | Large areas or whole homes |
| Heat Delivery Speed | Instant | Slow to Medium |
| Maintenance | Low | Medium to High |
Evaluating Heating Needs
It’s also crucial to think about your specific heating needs. The right choice will depend on the size and type of space you wish to heat, as well as your usage patterns.
Small Spaces
For small spaces like single rooms, dry space heaters generally excel. They provide quick, targeted heating without consuming too much power. Infrared heaters can be particularly effective, as they warm the people and objects directly within the room.
Large Spaces
If you need to heat a large space or multiple rooms, traditional heaters might be a better choice. Central heating systems are designed to distribute heat evenly across large areas, creating a more consistent indoor climate. While they might take longer to reach the desired temperature, the overall warmth can be more pleasant and encompassing.
Flexibility and Mobility
Dry space heaters are often portable, providing more flexibility. You can move an infrared or ceramic heater from your living room to your bedroom without much hassle, making them a versatile option for different rooms throughout the day.
Traditional heaters, especially built-in systems like central heating, are fixed installations. They’re less flexible but provide a more permanent solution for whole-house heating.
Heating Comparison Summary
| Feature | Dry Space Heaters | Traditional Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Ideal Room Size | Small to Medium | Medium to Large |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Installation Requirement | Minimal | Often Professional |
| Coverage | Limited, Direct | Extensive, Uniform |
| Portability | High | None |
:strip_icc()/GettyImages-1390275521-17ac0280256e4687a862ba53775d9cc4.jpg)
This image is property of www.bhg.com.
Safety Concerns
Safety is another critical consideration. Heaters generate heat, which means they must be used responsibly to prevent accidents or hazards.
Safety Features of Dry Space Heaters
Dry space heaters are generally considered safe, particularly newer models with built-in safety features. Many include overheat protection, tip-over switches, and cool-to-the-touch surfaces. Their portability makes storing them away from children and pets easier as well.
Safety Features of Traditional Heaters
Traditional heaters also come with safety features, but there are more variables to consider. For example, gas heaters require proper ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide buildup, and electric heaters need regular maintenance to ensure they don’t become fire hazards.
Safety Comparison Summary
| Feature | Dry Space Heaters | Traditional Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Built-in Safety Features | High | Medium to High |
| Tip-over Protection | Common | Rare |
| Fire Hazard Potential | Low | Medium to High |
| Ventilation Requirement | None | Necessary for some types |
Cost Analysis
When deciding between dry space heaters and traditional heaters, understanding the cost implications of each can be incredibly helpful.
Initial Costs
Dry space heaters tend to have a higher initial cost than some traditional heaters, like simple electric models. Infrared and ceramic heaters, especially high-quality ones, can be pricey, but the efficiency and convenience often offset the upfront cost.
Traditional heaters like central heating systems or gas heaters might seem cheaper initially, but installation costs can add up quickly. Professional installation may be required, particularly for whole-house systems.
Operating Costs
Operating costs can differ significantly between the two. Dry space heaters often have lower running costs due to their high efficiency. Traditional heaters, especially older models, can rack up higher energy bills.
Maintenance Costs
Maintenance is another factor to consider. Dry space heaters typically require minimal maintenance, while traditional heaters like central heating systems often need regular service checks, adding to the long-term costs.
Cost Comparison Summary
| Cost Factor | Dry Space Heaters | Traditional Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | High | Medium |
| Installation Cost | Minimal | High |
| Operating Cost | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Medium |

This image is property of www.electronicshub.org.
Environmental Impact
With growing awareness about sustainability and environmental impact, it’s important to consider how your choice affects the planet.
Environmental Impact of Dry Space Heaters
Dry space heaters like infrared models are generally more eco-friendly due to their efficiency. They consume less electricity for the same amount of heat, reducing your carbon footprint.
Environmental Impact of Traditional Heaters
Traditional heaters, particularly those that burn fossil fuels like gas or wood, have a greater environmental impact. Emissions from these systems contribute to air pollution and global warming. Electric traditional heaters, while cleaner, typically consume more energy, making them less eco-friendly compared to their dry space counterparts.
Environmental Comparison Summary
| Feature | Dry Space Heaters | Traditional Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Footprint | Low | High |
| Energy Consumption | Low | Medium to High |
| Emissions | None | Can be high |
User Experience
At the end of the day, how you interact with your heater is essential.
User Satisfaction with Dry Space Heaters
Users appreciate the quick heat, portability, and generally lower operating costs of dry space heaters. Features like remote control operation, adjustable settings, and digital thermostats enhance user satisfaction.
User Satisfaction with Traditional Heaters
Traditional heaters win points for their ability to heat large areas and provide consistent warmth. Many modern systems come with smart features like programmable thermostats and integration with home automation systems, enhancing convenience and control.
User Experience Comparison Summary
| Feature | Dry Space Heaters | Traditional Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | High | Medium to High |
| Customization Options | High | High |
| Smart Features | Increasing | High |
| Portability | High | None |
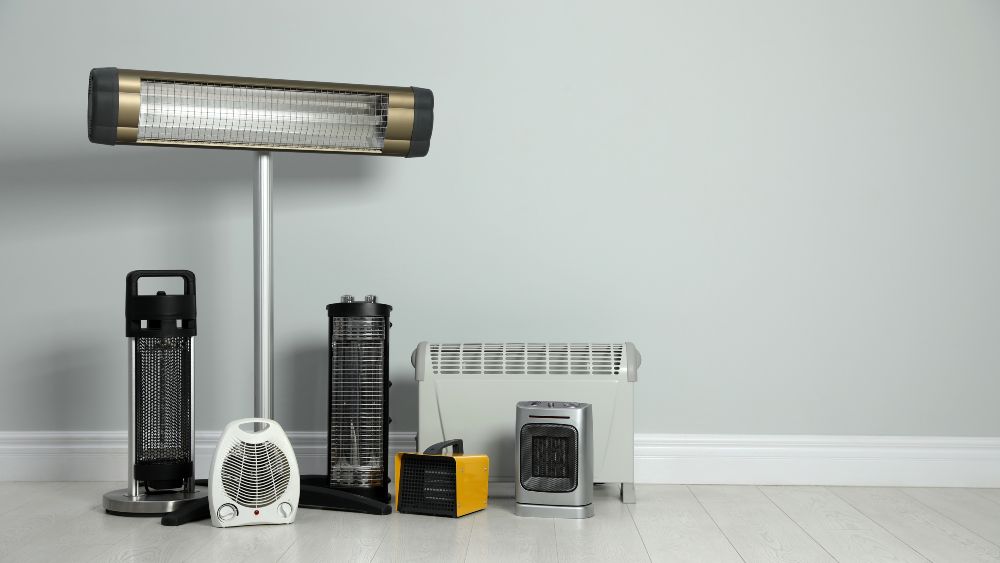

This image is property of cielowigle.com.
Making the Final Decision
Ultimately, the choice between a dry space heater and a traditional heater depends on your specific needs, priorities, and home setup.
Best For Dry Space Heaters
If you value energy efficiency, eco-friendly operation, and heating small spaces quickly, a dry space heater might be for you. The portability and low maintenance add to their appeal.
Best For Traditional Heaters
If you need to heat a larger home or require uniform warmth throughout multiple rooms, traditional heaters would probably serve you better. The initial higher cost and ongoing maintenance are balanced by their broader coverage and longevity.
Decision-Making Guide
| Situation | Recommended Heater |
|---|---|
| Small, individual rooms | Dry Space Heater |
| Large or multiple rooms | Traditional Heater |
| Focused, immediate heat | Dry Space Heater |
| Consistent, whole-house heat | Traditional Heater |
| Environmental concerns | Dry Space Heater |
| Budget constraints | Traditional Heater (short-term) |
Conclusion
Choosing the right heating solution for your home involves weighing various factors—including energy efficiency, cost, safety, environmental impact, and user experience. Both dry space heaters and traditional heaters have their unique benefits and downsides. By evaluating what matters most to you and considering the specifics of your living space, you can make a well-informed choice that ensures comfort and efficiency through the chilly months ahead.
